How Can Spinal Stenosis Be Treated?
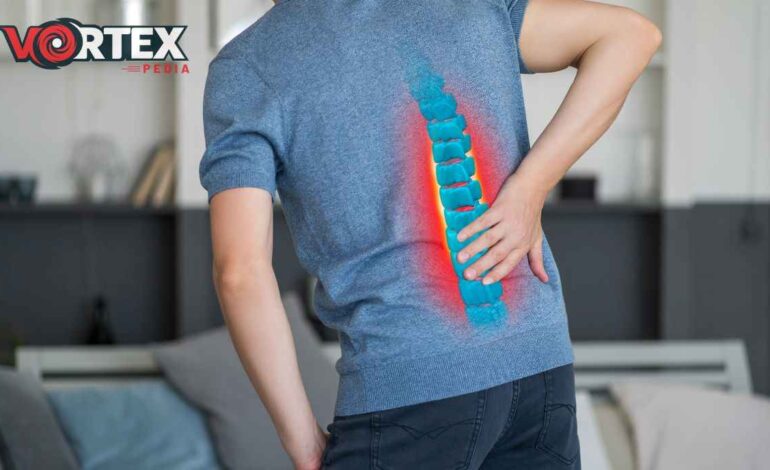
Our blogger “vortexpedia” will describe you in this article “How Can Spinal Stenosis Be Treated”? Spinal stenosis is a condition which is distinguished by the constriction of the spaces within the spine, leading to pressure on the nerves traveling through the spinal canal.
This often results in pain, numbness, or weakness, primarily in the legs and lower back. Treatment for spinal stenosis aims to alleviate symptoms, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
The approach to treatment can vary, ranging from conservative measures to surgical treatments, depending on how severe the symptoms are and individual health factors.
Conservative Treatment Options:
- Physiotherapy:
⦁ Physiotherapy is the main focus point of conservative treatment for the spinal stenosis disorder. Specially designed custom-based exercises help strengthen the core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote better posture.
⦁ Physiotherapists can tailor programs to the individual’s needs, addressing specific weaknesses and providing relief from symptoms.
- Medications:
⦁ Pain management through medications is a common component of conservative treatment.
⦁ Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help in lowering down the levels of inflammation and alleviating pain. In some cases, muscle relaxants or analgesics may also be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
⦁ Making lifestyle adjustments can significantly contribute to managing spinal stenosis. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine, while activities like swimming or cycling may be preferred over high-impact exercises.
⦁ Spreading awareness on maintaining posture and refraining from longer hours of standing or sitting can also play a vital role in symptom management.
- Assistive Devices:
⦁ Devices like braces or canes may be recommended to provide support and stability, especially during periods of increased symptoms.
⦁ These aids can assist in reducing strain on the spine and promoting better mobility.
- Epidural Steroid Injections:
⦁ In cases where conservative measures alone are not sufficient, epidural steroid injections may be taken into account.
⦁ Administered directly into the affected area, these injections aim to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
Advanced Treatment Options:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
⦁ Minimally invasive treatments that include processes, such as epiduroscopy or lumbar decompression, may be considered for those who do not respond adequately to conservative measures.
⦁ These procedures include smaller incisions, lessening of disruption of tissues, and a quicker healing process as in comparison with traditional ways of doing open surgery.
- Radiofrequency Ablation:
⦁ Radiofrequency ablation (also known as fulguration) targets specific nerves that cause pain.
⦁ By using heat generated from radiofrequency waves, the procedure disrupts nerve signals, providing relief from pain without major surgery.
- Specialized Ortho Care:
⦁ Some ortho-related activities may put all of their attention on the alignment of the spine to lessen the pressure on the nerves.
⦁ While results can differ, some individuals experience relief from spinal stenosis symptoms.
- Acupuncture:
⦁ Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate nerves and promote natural pain relief.
⦁ While research on acupuncture for spinal stenosis is ongoing, some individuals report symptom improvement.
Surgical Treatment:
- Decompressive Surgery:
⦁ When conservative measures and minimally invasive procedures fail to provide relief, surgical options may be considered.
⦁ Decompressive surgery, such as laminectomy or laminotomy, involves removing a portion of the spinal canal to create more space for the nerves. This helps alleviate pressure and reduce symptoms.
- Spinal Fusion:
⦁ Spinal fusion aims to stabilize the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae together.
⦁ This procedure may be recommended in cases where instability is contributing to spinal stenosis.
⦁ Fusion can limit movement in the affected area but may also reduce pain.
- Artificial Disc Replacement:
⦁ In selected cases, where only a single disc is affected, artificial disc replacement may be considered.
⦁ This surgical procedure involves removing the damaged disc and replacing it with an artificial one, preserving motion in the spine.
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation:
Regardless of the chosen treatment modality, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process.
Physiotherapy is often carried on post-surgery to help in restoring strength, improving flexibility levels, and the overall functionality. Patients are being taught proper body mechanics and the exercises that are needed to maintain the health of the spine.
Collaborative Approach:
The treatment of spinal stenosis often requires a collaborative approach involving orthopedic surgeons, neurosurgeons, pain specialists, physiotherapists, and other medical practitioners.
A thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, imaging studies, and response to conservative measures guides the decision-making process.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choices:
- Severity of Symptoms:
⦁ The intensity and impact of spinal stenosis symptoms influence the choice of treatment. Severe symptoms that significantly affect daily life may necessitate more aggressive approaches of treatment.
- Underlying Health Conditions:
⦁ The presence of other health constraints can leave an impact on the suitability of specific treatment plans. Individual health factors, like one’s age and their overall fitness level, are prudently taken into consideration.
- Patient Preferences:
⦁ Patient preferences and goals are integral to the decision-making process. Some individuals may prioritize non-surgical approaches, while others may opt for surgical treatments for faster relief.
- Risk Tolerance:
⦁ The possible complications, risk factors involved and the advantages associated with each treatment option plan are well conveyed to the patient.
⦁ Factors such as the invasiveness of the procedure, recovery time, and potential complications play a crucial role in decision-making.
Conclusion:
The management of spinal stenosis is individualized because every patient is different and has different progressing conditions. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to mediation; or at least, there shouldn’t be. This starts with the consultation with a top spinal surgeon in Delhi who will determine the level of discomfort, general health, and patient’s values. An initial evaluation plays a critical role, especially because of the necessity to tailor the treatment plan to particular requirements.
The treatment of this disease ranges from conservative to minimally invasive procedures and can go up to surgical procedures. The overall aims of these treatments are to relieve pains and inflammation, improve the range of motion of the individual’s spine and thus the ability to move around more comfortably, and in summary to provide a better quality of life for the affected people with spinal stenosis.
To this extent, therefore, the role of ongoing management cannot be understated since it is also an important tool. Subsequent visits to your spine specialist in Delhi, in addition to making vitally important lifestyle changes will greatly enhance the overall wellbeing of your spine. For such details and individual consultation, the patient is advised to visit a top cervical pain doctor in Delhi. They will assist you in getting the best treatment and care for your ailment as per the recommendations of the licensing authorities.